Tutorial for distance on-line learning (by EDUMOTIVA)
2. Review of online tools and e-learning practices towards optimal learning experiences in higher education.
2.2. Asynchronous teaching tools
Asynchronous e-Learning platforms work supplementary to synchronous online teaching or can they be used as standalone tools supportively to face to face teaching. In higher educational institutes such of tools were already implemented in order to support learning process. Due to pandemic and distance learning enforcement, asynchronous platforms become even more crucial for teachers and students. Many platforms have been adopted to support teachers and students like Moodle, Google Classroom, Open eClass, Canvas, Blackboard and edX.
Google as a leading giant on the Internet, offers, with out of charge, Google Classroom (https://classroom.google.com/) for asynchronous teaching which integrates Google Drive as storage. This results, that teacher can use any of Google’s Drive tools to create documents and being assigned to the students. Moreover, Blackboard Learn (https://www.blackboard.com) constitutes a good alternative for asynchronous platform providing many features, yet pricing policy does not include any free license. Furthermore, Open edX (https://open.edx.org/) is an open source platform which is created by MIT and Harvard University, aiming to spread knowledge into public by massive open online courses (MOOC). The latest platform, can be utilized by higher education to engage students to the learning process, lean on the quantity of the available tools. Following the same philosophy as the previous platform, Coursera (https://www.coursera.org/), which was founded by Stanford University to provide quality MOOC that leads to certificates. Coursera can be exploited as asynchronous platform in order to support distance online learning. World’s most well-known platform is Moodle (https://moodle.org/) which is an open source web-based platform that follows client-server architecture. Is considered as a Learning Management System (LMS) meaning that is created aiming to support and extend online/distance learning procedure. Canvas (https://www.instructure.com/en-gb/product/canvas/higher-ed) is also a web-based LMS platform, follows same architecture as Moodle. The Greek Universities Network has develop its own proposal for asynchronous e-Learning services named Open eClass (https://www.openeclass.org/). Open eClass is widely spread in Greek academic community but it is also available in many languages such as English, Spanish, French, German and Italian. It is an open source and web-based, as the aforementioned platforms, and it is supported by the Greek Universities network (GUnet). Moodle, Canvas and Open eClass considering their acceptance by the academic community will be examined more detailed in the following paragraphs.
Moodle, as a pure LMS platform, implements all the features needed for asynchronous distance learning. Teacher can create courses and students can choose to enroll at any accessible course. Tools such as chat, calendar, forum, assignments, feedback and wiki are some of Moodle’s features to encourage collaboration and increase students’ engagement towards learning procedure. Teacher can create a series of learning activities, knowing as learning path, that students must follow, whereas their progress would be monitored.
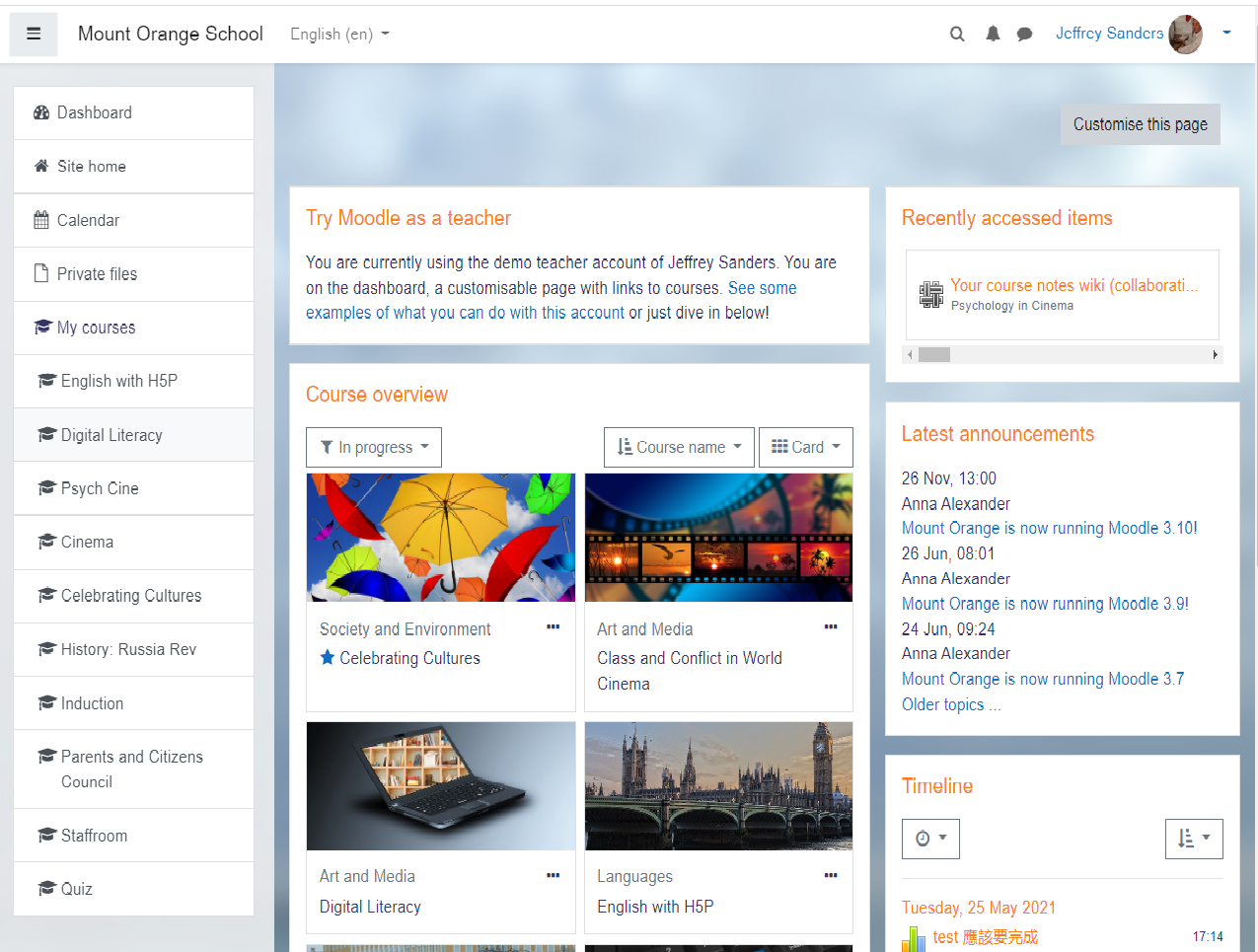
Moodle’s interface can be characterized as user friendly although sometimes the plenty of options leads to the opposite result. An experience user will exploit all the given preferences while a beginner might be confused. Some features that Moodle supports are:
· Assignments
· Chat
· Choice
· Database
· Feedback
· Forum
· Glossary
· Lesson
· Quiz
· Survey
· Wiki
· Workshop
· Learning path (SCORM)
Platform’s administrator, “teacher” and “student” are the three main accounts that Moodle defines although “manager”, “course creator” and “non-editing teacher” are extra types of accounts which also are defined. Moodle is distributed under the GNU General Public License (GPL) which means that any institute or organization can install it on its server and run Moodle platform. Additionally, unlike other LMS platforms, Moodle gives the option to the customer to run Moodle through https://moodle.org cloud at a given cost relieving from hardware and administration cost.
The Open eClass platform has been designed, by Greek Universities network, for asynchronous e-Learning purposes hence, it is considered as an LMS. Same way like Moodle, courses can be created by teacher while students can enroll/follow any course for which they are eligible based on their account privileges’.
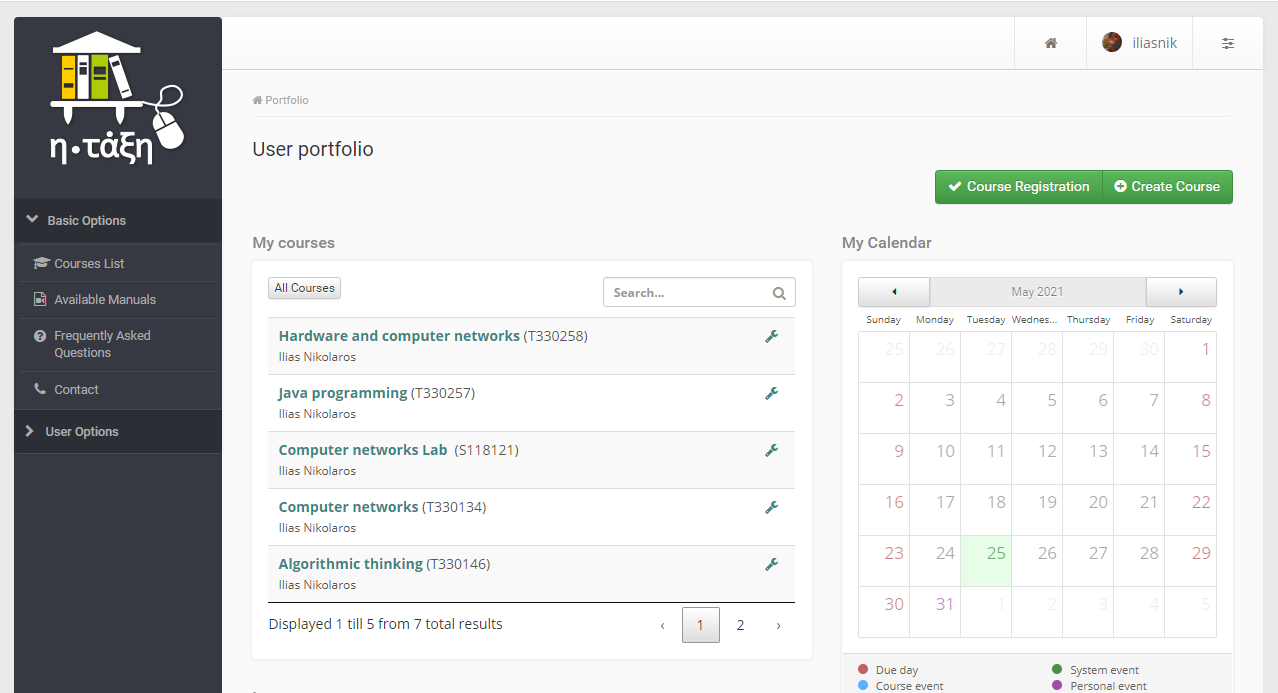
Open eClass’ environment is user friendly, providing many tools for teacher in order to create dynamic educational activities. Such tools are:
· Agenda
· Documents
· Announcements
· Forums
· User Groups
· Links
· Assignments
· Self- evaluation exercises
· Glossary
· E-book
· Multimedia
· Learning path
· Wiki questionnaires
At this point must be highlighted that Open eClass offers less options than Moodle, however fist one has more easy menu.
A beginner user may prefer Open eClass as a result of its less complexity compared to Moodle. Except platform’s administrator two main user types are supported which are “teacher” and “student” while “teacher assistant” and “group leader” are auxiliary type of users. Open eClass platform is distributed free as open source software. Any installation must be supported by the person/organization to whom it belongs.
Canvas is a wide spread LMS platform in higher education designed to enhance students engagement during asynchronous e-Learning and it is addressed particularly for educational purposes. Canvas’ features include Outcomes, MasteryPaths, Speedgrader, Mastery GradeBook, and Canvas Parent. MasteryPaths is a powerful tool which allows content automatically be released to the students based on their prior performance.
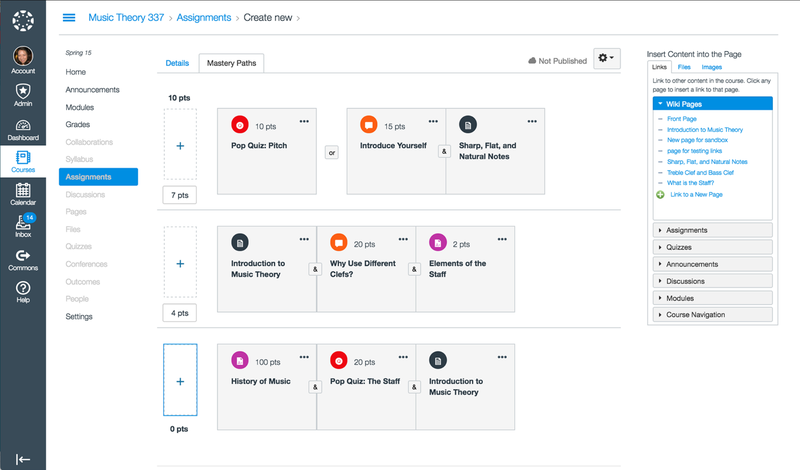
Despite the fact that Canvas is a modern and fresh looking platform with a user friendly interface, Moodle is by far more powerful. User has limited customization control in courses’ tools and interface. Third party tools are easily incorporate and cooperate with Canvas giving teacher the benefit to integrate popular applications.
Even though Canvas is an open source web based platform, educational institutes must pay in order to install the platform in a private server or use the Canvas’ cloud for hosting their LMS while the exact fee depends on how large the organization is. There are also two free licenses, one for a two weeks free trial and one, unlimited time, for a single teacher who wants to work with this particular platform.
In the bottom line the three asynchronous LMS platforms have many similarities. All follow cloud architecture, are web based, support multilingual environment, are open source and their license is modeled as SaaS (Software as a Service). The three platforms have available applications for Android and iOS with Open eClass’ application facing some crushes and being the most outdated. Amongst the three asynchronous LMS platforms Moodle is the more powerful. Teacher using Moodle, has the opportunity to maximize distance e-Learning effectiveness. The goal which is to engage students having the appropriate tools following their progress is achieved. Gives more than enough options for customization, has many tools, its menu is user friendly and can be installed for free while paid services are offered supplementary. Moodle’s only drawback is its complexity when user attempt to exploit all of its capabilities. Open eClass is a simple alternative to Moodle. Its menu is easy, has all the necessary tools for managing asynchronous teaching and is also free distributed. Canvas is similar to Moodle, with modern and prettier interface which makes students’ interaction with it more attractive. Its free license covers only one individual person, hence any educational institute has to pay in order to install it.