Activity 3. Thermometer (TMP36)
The purpose of this activity is for the microcontroller to use the built-in ADC and read the TMP36 sensor.
(50 minutes)
Activity 3
The PIC18F4550:
- reads the analog voltage of the sensor and converts it to a value (0~1023)
- converts the ADC value to analog voltage
- converts analog voltage to temperature (oC)
- displays the temperature on a LCD
- turns ON/OFF the 8 LEDs, according to the following table
Table 1. Temperature and LEDs
|
Temperature (oC) |
Active LEDs |
|
< 0 |
None |
|
< 10 |
LED1 |
|
< 20 |
LED1 ~ LED2 |
|
< 30 |
LED1 ~ LED3 |
|
< 40 |
LED1 ~ LED4 |
|
< 50 |
LED1 ~ LED5 |
|
< 60 |
LED1 ~ LED6 |
|
< 70 |
LED1 ~ LED7 |
|
> 70 |
LED1 ~ LED8 |
Step 1. The circuit is drawn at the Proteus Design Suite.
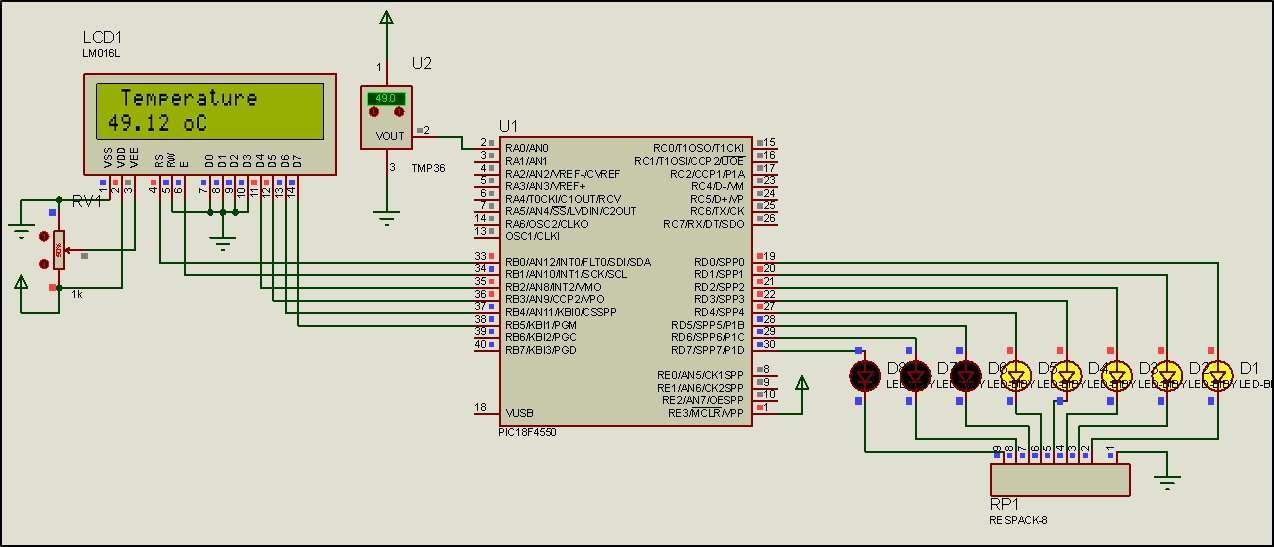
Step 2. The program in C language is written.
Write in CCS C Compiler the program in C language
#include <main.h> // the file main.h with the
// initial settings is included.
// This file must be placed in the same
// folder with the project.
// Also the 18F4550.h file must exist
// in the same folder with the project
#include <flex_lcd.h> // The h file of the lcd driver
// should be in the same folder where we will save our program.
// The #define LCD_DB4 PIN_B4 etc statements in flex_lcd.c
// should be checked and possibly modified.
// These statements determine the pins of the microcontroller
// that are connected to LCD 16x2.
#byte PORTB =0xF81
// We attribute to the memory position 0xF81 the name PORTB.
// This means that we define a 8 bit variable whose value
// will be stored to the memory position F81h.
// The memory position F81h is the PORTD data register.
#byte PORTD =0xF83
// We attribute to the memory position 0xF83 the name PORTD.
// This means that we define a 8 bit variable whose value
// will be stored to the memory position F83h.
// The memory position F83h is the PORTD data register.
unsigned int16 ADC_value; //ADC = 10 Bit => values: 0~1023
float voltage; //variable to store the sensor's (TMP36) analog voltage
float temperature; //variable to store sensor's temperature
// ********* main program ************************
void main() {
set_tris_b(0x00); //PORTB is defined as output
set_tris_d(0x00); //PORTD is defined as output
lcd_init(); //initialization routine for the LCD 16x2
setup_adc(ADC_CLOCK_DIV_8); // Set ADC conversion time to 8Tosc
setup_adc_ports(AN0); // Set RA0 as analog pin
set_adc_channel(0); // Select channel 0 (Analog input 0)
while(TRUE) {
delay_ms(1000); //wait for 1 sec
lcd_putc("\f"); //clear the screen
lcd_putc(" Temperature"); //send a message to the LCD
lcd_gotoxy(1,2); //first position of the second line
ADC_value=read_adc(); //read value from ADC
voltage = ((float)(ADC_value*5)/1024); //convert adc value to analog voltage
voltage*=1000; //convert V to mV
temperature = (voltage-500)/10;//convert sensor's voltage (mV) to temperature (oC)
printf(lcd_putc,"%f oC",temperature); //send a message to the LCD
//turn ON / OFF LEDs according to temperature
if(temperature<0){
PORTD=0b00000000;
}
else if(temperature<10){
PORTD=0b00000001;
}
else if(temperature<20){
PORTD=0b00000011;
}
else if(temperature<30){
PORTD=0b00000111;
}
else if(temperature<40){
PORTD=0b00001111;
}
else if(temperature<50){
PORTD=0b00011111;
}
else if(temperature<60){
PORTD=0b00111111;
}
else if(temperature<70){
PORTD=0b01111111;
}
else{
PORTD=0b11111111;
}
}
Step 3. Compile the program in order to create the hex.file (program in machine code). Load the program (hex.file) to the microcontroller.
Step4. Run the simulation and check the correct operation of the circuit.
Step5. Suggested modifications and discussion:
- can the LCD show temperature in Kelvin and Celsius at the same time?
source 1